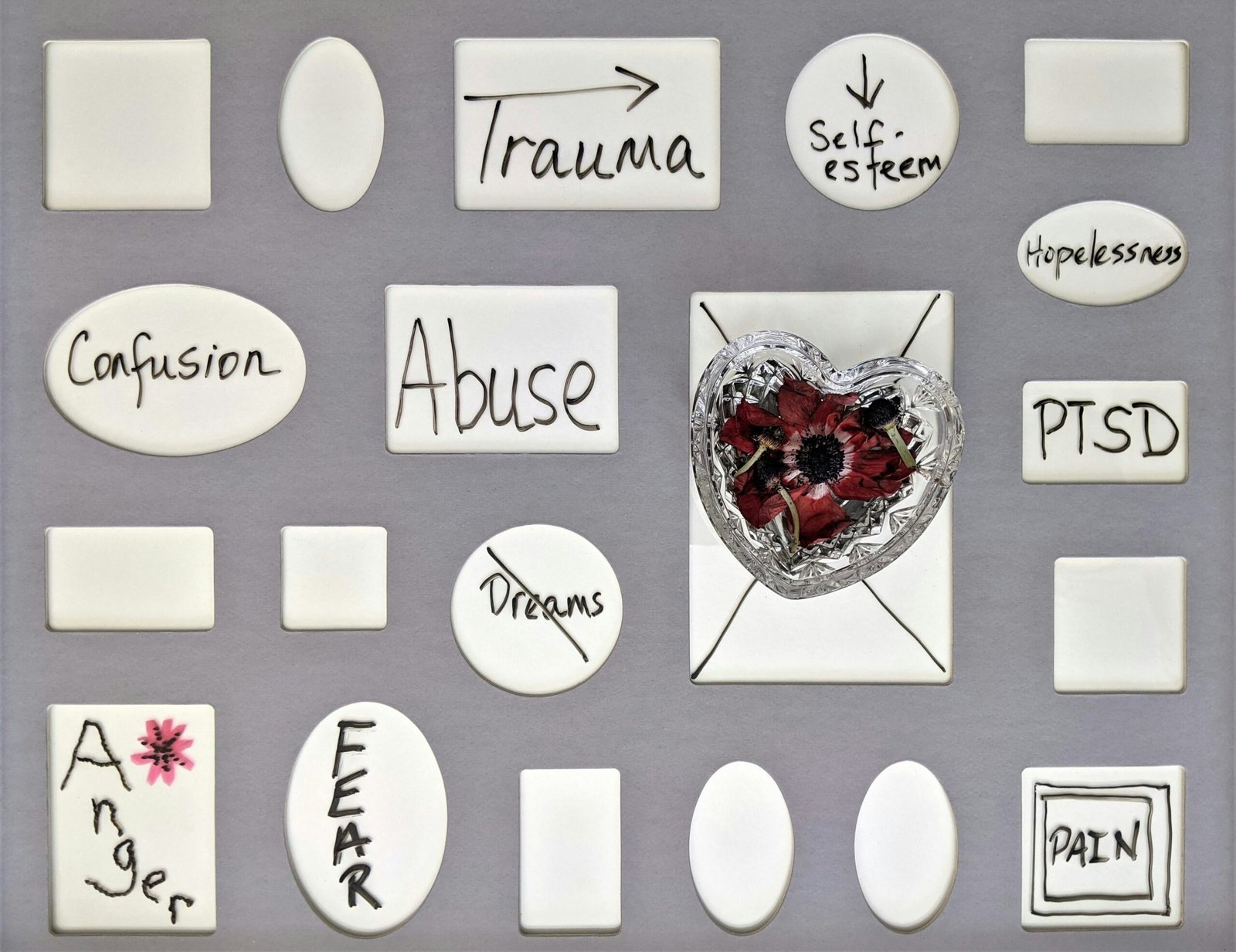
When we talk about trauma, it is important to understand that it can come in many forms. It could be a single event, such as a car accident or a natural disaster, or it could be a series of events, like ongoing abuse or neglect. Trauma can also be categorized as either acute or complex. Acute trauma refers to a single traumatic event, while complex trauma refers to repeated or prolonged exposure to traumatic experiences.
The impact of trauma on mental well-being can be profound. People who have experienced trauma may develop symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), such as intrusive thoughts, nightmares, flashbacks, and avoidance of reminders of the traumatic event. They may also experience high levels of anxiety, depression, and difficulty regulating their emotions. Additionally, trauma can affect one’s sense of self and interpersonal relationships, leading to difficulties in trust, intimacy, and forming connections with others.
Coping with trauma requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both the psychological and physical aspects of healing. One important aspect is seeking professional help. Therapists who specialize in trauma can provide a safe and supportive environment for individuals to process their experiences and develop coping strategies. Different therapeutic modalities, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), and somatic experiencing, can be effective in helping individuals heal from trauma.
In addition to therapy, self-care practices play a crucial role in navigating trauma. Engaging in activities that promote relaxation and stress reduction, such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises, can help regulate the nervous system and promote a sense of calm. Taking care of one’s physical health through regular exercise, nutritious eating, and adequate sleep is also important in supporting overall well-being.
Building a support network is another crucial component of healing from trauma. Connecting with trusted friends, family members, or support groups can provide a sense of belonging and understanding. Sharing one’s experiences and feelings with others who have gone through similar situations can be validating and empowering.
Lastly, it is important to remember that healing from trauma is a journey that takes time. Each person’s experience is unique, and the healing process may involve ups and downs. It is normal to have setbacks, but with the right support and coping strategies, it is possible to move forward and rebuild a fulfilling and meaningful life.
Understanding Trauma
Trauma can be defined as a deeply distressing or disturbing experience that overwhelms an individual’s ability to cope. It can result from various events such as physical or sexual abuse, natural disasters, accidents, or witnessing violence. Traumatic experiences are subjective, and what may be traumatic for one person may not be for another. It is important to recognize that trauma can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background.
When someone goes through a traumatic event, their sense of safety and security is shattered. They may experience intense fear, helplessness, or horror. These emotions can lead to a wide range of physical, emotional, and psychological reactions. Common symptoms of trauma include:
- Flashbacks or intrusive memories
- Nightmares or sleep disturbances
- Emotional numbness or detachment
- Hyperarousal or hypervigilance
- Avoidance of reminders of the trauma
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Changes in appetite or weight
- Feeling irritable or easily startled
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms following a traumatic event, it is important to seek professional help. Trauma can have a profound impact on mental well-being, and early intervention can make a significant difference in the healing process.
It is crucial to understand that trauma is not just limited to the immediate aftermath of a distressing event. Its effects can linger long after the event has occurred, sometimes manifesting in unexpected ways. For example, individuals who have experienced trauma may develop anxiety disorders, depression, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
PTSD is a specific type of anxiety disorder that can develop after a traumatic event. It is characterized by intrusive thoughts, nightmares, and flashbacks related to the traumatic experience. Individuals with PTSD may also experience intense emotional distress when exposed to reminders of the trauma, leading to avoidance behaviors.
Furthermore, trauma can have a significant impact on an individual’s relationships and social functioning. It can cause difficulties in forming and maintaining healthy relationships, as well as hinder one’s ability to trust others. Additionally, individuals who have experienced trauma may exhibit self-destructive behaviors, such as substance abuse, as a way to cope with their emotional pain.
It is important to approach trauma with sensitivity and understanding. Providing a safe and supportive environment for individuals who have experienced trauma can greatly aid in their healing process. This can involve offering empathy, active listening, and validating their experiences. Additionally, encouraging them to seek professional help from therapists or counselors who specialize in trauma can be beneficial.
Overall, trauma is a complex and multifaceted experience that can have long-lasting effects on an individual’s well-being. By increasing awareness and understanding, we can create a more compassionate and supportive society for those who have experienced trauma.
The Impact of Trauma on Mental Health
Trauma can have a wide range of effects on mental health, and its impact can vary from person to person. Some individuals may develop post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), a specific mental health condition that can occur after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. PTSD is characterized by intrusive thoughts, nightmares, and flashbacks related to the trauma, as well as emotional and physical reactions triggered by reminders of the event.
However, not everyone who experiences trauma will develop PTSD. Some individuals may experience other mental health challenges such as depression, anxiety, substance abuse, or dissociative disorders. Trauma can also affect interpersonal relationships, self-esteem, and overall quality of life.
One of the ways trauma can impact mental health is through the development of anxiety disorders. Anxiety disorders can manifest as excessive worry, restlessness, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and sleep disturbances. These symptoms can significantly interfere with daily functioning and overall well-being. Moreover, individuals who have experienced trauma may develop specific phobias, such as a fear of certain places or situations that remind them of the traumatic event.
Depression is another common mental health issue that can arise as a result of trauma. It is characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, emptiness, and a loss of interest in activities that were once enjoyable. Trauma can trigger a cascade of negative emotions, leading to a sense of hopelessness and despair. In severe cases, individuals may experience thoughts of self-harm or suicide.
Substance abuse is also a significant concern for individuals who have experienced trauma. Many people turn to drugs or alcohol as a way to cope with the distressing memories and emotions associated with their traumatic experiences. Substance abuse can exacerbate existing mental health issues and lead to a cycle of addiction and further trauma.
In addition to these specific mental health challenges, trauma can also have a profound impact on interpersonal relationships. Individuals who have experienced trauma may struggle with trust, intimacy, and forming meaningful connections with others. They may have difficulty expressing their emotions or may become overly dependent on others for support. These challenges can strain relationships and lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
Furthermore, trauma can significantly impact an individual’s self-esteem and overall sense of self-worth. Survivors of trauma may blame themselves for the event or feel a deep sense of shame and guilt. They may also struggle with feelings of worthlessness or have a distorted self-image. These negative beliefs about oneself can hinder personal growth and hinder the ability to engage in healthy, fulfilling relationships.
In conclusion, trauma can have a profound and lasting impact on mental health. It can lead to the development of specific mental health conditions such as PTSD, anxiety disorders, depression, and substance abuse. Trauma can also affect interpersonal relationships, self-esteem, and overall quality of life. It is essential for individuals who have experienced trauma to seek professional help and support to address their mental health needs and begin the healing process.
7. Educate Yourself
One way to cope with and heal from trauma is to educate yourself about the effects of trauma and the various resources available. This can help you better understand your own experiences and provide insight into the healing journey. Books, articles, and online resources can provide valuable information and guidance.
8. Engage in Physical Activity
Physical activity has been shown to have numerous benefits for mental health, including trauma recovery. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood boosters, and can help reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression. Engaging in activities such as jogging, swimming, or dancing can provide a healthy outlet for emotions and promote overall well-being.
9. Practice Mindfulness
Mindfulness involves being fully present in the moment and non-judgmentally observing one’s thoughts and feelings. This practice can help individuals become more aware of their triggers and reactions to trauma, allowing them to respond in a more grounded and intentional manner. Mindfulness can be cultivated through meditation, breathing exercises, or simply paying attention to the present moment.
10. Engage in Creative Expression
Expressing oneself creatively can be a powerful tool for healing from trauma. Writing, painting, dancing, or playing a musical instrument can provide an outlet for emotions and allow individuals to process their experiences in a non-verbal way. Engaging in creative expression can also foster a sense of empowerment and self-discovery.
11. Practice Gratitude
Gratitude has been shown to have a positive impact on mental well-being and can be particularly helpful in the healing process. Taking time each day to reflect on and express gratitude for the positive aspects of life can help shift focus away from the trauma and promote a more positive mindset. This can be done through journaling, creating a gratitude jar, or simply sharing gratitude with loved ones.
Overall, coping and healing from trauma is a unique and individual process. What works for one person may not work for another, so it is important to approach the healing journey with an open mind and a willingness to explore different strategies. With time, support, and self-care, it is possible to find healing and regain a sense of well-being after experiencing trauma.


